¶ Installation et utilisation de Podman
¶ Références
https://podman.io/docs/installation
https://docs.podman.io/en/latest/Tutorials.html
¶ Environnement
OS: Debian 13 Installation minimum + serveur SSH
KVM : pod sur bv01
FQDN: pod.infra.bv.stef.lan
IP: 192.168.200.28
GW: 192.168.200.254
DNS: 192.168.200.254
¶ Installation
root@pod:~# apt install podman -y
Installation de :
podman
Installation de dépendances :
aardvark-dns libisl23
buildah libksba8
ca-certificates libldap-common
catatonit libldap2
conmon libmpc3
containernetworking-plugins libmpfr6
containers-storage libnet1
cpp libnetfilter-conntrack3
cpp-14 libnfnetlink0
cpp-14-x86-64-linux-gnu libnl-3-200
cpp-x86-64-linux-gnu libnpth0t64
criu libp11-kit0
crun libprotobuf-c1
dirmngr libprotobuf32t64
fuse-overlayfs libpython3-stdlib
fuse3 libpython3.13-minimal
gnupg libpython3.13-stdlib
gnupg-l10n libsasl2-2
gnupg-utils libsasl2-modules
golang-github-containers-common libsasl2-modules-db
golang-github-containers-image libslirp0
gpg libsubid5
gpg-agent libtasn1-6
gpg-wks-client libyajl2
gpgconf media-types
gpgsm netavark
gpgv openssl
iptables passt
libassuan9 pinentry-curses
libcompel1 python3
libcriu2 python3-minimal
libgcrypt20 python3-protobuf
libgnutls30t64 python3-pycriu
libgpg-error-l10n python3.13
libgpg-error0 python3.13-minimal
libgpgme11t64 slirp4netns
libip4tc2 uidmap
libip6tc2
Paquets suggérés :
cpp-doc tpm2daemon docker-compose
gcc-14-locales firewalld python3-doc
cpp-14-doc rng-tools python3-tk
libwasmedge0 gnutls-bin python3-venv
pinentry-gnome3 libsasl2-modules-gssapi-mit python3.13-venv
tor | libsasl2-modules-gssapi-heimdal python3.13-doc
gpg-wks-server libsasl2-modules-ldap binutils
parcimonie libsasl2-modules-otp binfmt-support
xloadimage libsasl2-modules-sql
scdaemon pinentry-doc
...
Ajout
sudo apt-get install -y \
libapparmor-dev \
fuse-overlayfs
¶ Premiers Tests
¶ Lancement d'un pod
sudo podman run -dt -p 8080:80/tcp docker.io/library/httpd
¶ Liste des pods
sudo podman ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
stef@pod:~$ sudo podman ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
2e89c1f01a8a docker.io/library/httpd:latest httpd-foreground 2 minutes ago Exited (0) 4 seconds ago 0.0.0.0:8080->80/tcp
stef@pod:~$ curl 127.0.0.1:8080
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<title>It works! Apache httpd</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>It works!</p>
</body>
</html>
<html>
¶ Création d'un checkpoint d'un pod
stef@pod:~$ sudo podman container checkpoint 2e89c1f01a8a
2e89c1f01a8a
stef@pod:~$ sudo podman ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
2e89c1f01a8a docker.io/library/httpd:latest httpd-foreground 5 minutes ago Exited (0) 6 seconds ago 0.0.0.0:8080->80/tcp wizardly_williamson
¶ Relance checkpoint du pod
stef@pod:~$ sudo podman container restore 2e89c1f01a8a
¶ Migration d'un pod
¶ Création du fichier de checkpoint
sudo podman container checkpoint 2e89c1f01a8a -e /tmp/checkpoint.tar.zst
¶ Destruction du pod original
stef@pod:~$ sudo podman rm 2e89c1f01a8a
2e89c1f01a8a
stef@pod:~$ sudo podman ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
¶ Restauration du pod a partir du fichier de checkpoint
stef@pod:~$ sudo podman container restore -i /tmp/checkpoint.tar.zst
stef@pod:~$ sudo podman ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
2e89c1f01a8a docker.io/library/httpd:latest httpd-foreground 5 seconds ago Up 5 seconds 0.0.0.0:8080->80/tcp wizardly_williamson
Si vous copiez le fichier de checkpoint vers une autre machine disposant de podman la restauration sera également possible. Ceci permet de migrer tres facilement des applications.
¶ Considération générale
La pluparts des fonctions podman ont les mémes nom que celles utilisés par docker.
Mais il en existe des spécifiques
| Podman | Docker |
|---|---|
|
artifact Manage OCI artifacts attach Attach to a running container auto-update Auto update containers according to their auto-update policy build Build an image using instructions from Containerfiles commit Create new image based on the changed container compose Run compose workloads via an external provider such as docker-compose or podman-compose container Manage containers cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem create Create but do not start a container diff Display the changes to the object's file system events Show podman system events exec Run a process in a running container export Export container's filesystem contents as a tar archive farm Farm out builds to remote machines generate Generate structured data based on containers, pods or volumes healthcheck Manage health checks on containers help Help about any command history Show history of a specified image image Manage images images List images in local storage import Import a tarball to create a filesystem image info Display podman system information init Initialize one or more containers inspect Display the configuration of object denoted by ID kill Kill one or more running containers with a specific signal kube Play containers, pods or volumes from a structured file load Load image(s) from a tar archive login Log in to a container registry logout Log out of a container registry logs Fetch the logs of one or more containers machine Manage a virtual machine manifest Manipulate manifest lists and image indexes mount Mount a working container's root filesystem network Manage networks pause Pause all the processes in one or more containers pod Manage pods port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container ps List containers pull Pull an image from a registry push Push an image to a specified destination rename Rename an existing container restart Restart one or more containers rm Remove one or more containers rmi Remove one or more images from local storage run Run a command in a new container save Save image(s) to an archive search Search registry for image secret Manage secrets start Start one or more containers stats Display a live stream of container resource usage statistics stop Stop one or more containers system Manage podman tag Add an additional name to a local image top Display the running processes of a container unmount Unmount working container's root filesystem unpause Unpause the processes in one or more containers unshare Run a command in a modified user namespace untag Remove a name from a local image update Update an existing container version Display the Podman version information volume Manage volumes wait Block on one or more containers |
run Create and run a new container from an image exec Execute a command in a running container ps List containers build Build an image from a Dockerfile bake Build from a file pull Download an image from a registry push Upload an image to a registry images List images login Authenticate to a registry logout Log out from a registry search Search Docker Hub for images version Show the Docker version information info Display system-wide information builder Manage builds buildx* Docker Buildx compose* Docker Compose container Manage containers context Manage contexts image Manage images manifest Manage Docker image manifests and manifest lists network Manage networks plugin Manage plugins system Manage Docker volume Manage volumes swarm Manage Swarm attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container commit Create a new image from a container's changes cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem create Create a new container diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem events Get real time events from the server export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive history Show the history of an image import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image inspect Return low-level information on Docker objects kill Kill one or more running containers load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN logs Fetch the logs of a container pause Pause all processes within one or more containers port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container rename Rename a container restart Restart one or more containers rm Remove one or more containers rmi Remove one or more images save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default) start Start one or more stopped containers stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics stop Stop one or more running containers tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE top Display the running processes of a container unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers update Update configuration of one or more containers wait Block until one or more containers stop, then print their exit codes |
¶ Les registries
Le podman search debian ne retourne rien !
podman search debian --limit 3
Contrairement a docker il faut spécifier une registry spécifique pour chercher une image
Exemple:
stef@pod:~$ podman search docker.io/debian --limit 3
NAME DESCRIPTION
docker.io/library/debian Debian is a Linux distribution that's compos...
docker.io/dockette/debian My Debian Sid | Jessie | Wheezy Base Images
docker.io/corpusops/debian debian corpusops baseimage
ou
stef@pod:~$ podman search quay.io/debian --limit 3
NAME DESCRIPTION
quay.io/jetstack/trust-pkg-debian-bookworm trust-manager trust bundle derived from the...
quay.io/jetstack/cert-manager-package-debian trust-manager trust bundle derived from the...
quay.io/prometheuscommunity/postgres-exporter [
Vérifications:
stef@pod:~$ cat /etc/subgid
stef:100000:65536
stef@pod:~$ cat /etc/subuid
stef:100000:65536
¶ Création et démarrage de l'acces à la socket podman spécifique à mon utilisateur
stef@pod:~$ systemctl --user start podman.socket
stef@pod:~$ systemctl --user enable podman.socket
Created symlink '/home/stef/.config/systemd/user/sockets.target.wants/podman.socket' → '/usr/lib/systemd/user/podman.socket'.
Je souhaite pouvoir utiliser les port 80 & 443 qui sont par défaut privilégiés
Je dois les rendre non privilégiés
sudo su -
root@pod:~# sysctl net.ipv4.ip_unprivileged_port_start=80
net.ipv4.ip_unprivileged_port_start = 80
Pour rendre la configuration persistante:
root@pod:~# echo "net.ipv4.ip_unprivileged_port_start=80" > /etc/sysctl.d/user_priv_ports.conf
Test de l'acces à la socket podman avec mon utilisateur
La variable XDG_RUNTIME_DIR pointe sur le répertoire contenant l'acces aux ressources rootless de mon user.
stef@pod:~/pods/traefik/log$ echo $XDG_RUNTIME_DIR
/run/user/1000
stef@pod:~/pods/traefik/log$ curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" --unix-socket /run/user/1000/podman/podman.sock http://localhost/_ping
OK
L'acces à la socket utilisateur est ok
La socket est bien sécifique a l'utilisateur, si on test avec un autre utilusateur ont ne peut acceder à la ressource:
test@pod:~$ curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" --unix-socket /run/user/1000/podman/podman.sock http://localhost/_ping
curl: (7) Failed to connect to localhost port 80 after 0 ms: Could not connect to server
¶ Deploiement Traefik en mode rootless
Contenu du répertoire /home/stef/pods/traefik:
├── conf
│ └── traefik.toml
├── docker-compose.yml
├── log
│ └── traefik.log
└── ssl
├── wildcard.bv.stef.lan-crt.pem
└── wildcard.bv.stef.lan-key.pem
¶ Fichier docker-compose.yml
La modification par rapport au fichier docker est le path de la socket utilisé.
on expose au container /run/user/1000/podman/podman.sock en tant que socket docker
Dans le cas de Docker ont doit utiliser la socket systeme /var/run/docker.sock
La socket est par contre toujours passée en tant que /var/run/docker.sock dans le container.
services:
traefik:
image: docker.io/library/traefik:latest
container_name: "traefik"
restart: always
command:
- "--entrypoints.insecure.address=:80"
- "--entrypoints.secure.address=:443"
- "--log.level=ERROR"
- --api
- "--api.insecure=true"
- "--providers.docker=true"
- "--providers.docker.exposedbydefault=false"
- "--providers.docker.watch=true"
- "--providers.docker.defaultrule=Host(`{{ .Name }}.bv.stef.lan`)"
- "--providers.file.directory=/etc/traefik/conf"
- "--log.filePath=/var/traefik/log/traefik.log"
- "--log.level=INFO"
ports:
- "80:80"
- "443:443"
volumes:
- /run/user/1000/podman/podman.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro
- ./conf:/etc/traefik/conf
- ./ssl:/ssl
- ./log:/var/traefik/log
labels:
# Dashboard
- "traefik.enable=true"
- "traefik.http.routers.traefik.rule=Host(`traefikpod.bv.stef.lan`)"
- "traefik.http.routers.traefik.service=api@internal"
- "traefik.http.routers.traefik.tls=true"
- "traefik.http.routers.traefik.entrypoints=secure"
- --providers.file.directory=/etc/traefik/conf
tinyauth:
image: ghcr.io/steveiliop56/tinyauth:v3
container_name: tinyauth
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
- SECRET=Q3YuwUjrlfXfqc4lPU2xTHjvG7rlxL2I
- APP_URL=https://tinyauthpod.bv.stef.lan
- USERS=stef:$$2a$$10$$I/QO3oJkpu/ZpEkBlDJCAebtyFtiVmZCpXCGJ4bHgFOhsdeOdAz6K
labels:
traefik.enable: true
traefik.http.routers.tinyauth.tls: true
traefik.http.routers.tinyauth.rule: Host(`tinyauthpod.bv.stef.lan`)
traefik.http.middlewares.tinyauth.forwardauth.address: http://tinyauthpod:3000/api/auth/traefik
networks:
default:
name: traefik
external: true
¶ Fichier conf/traefik.toml
Pas de modification à faire par rapport à docker vue que ce fichier est lié au container lui meme.
[global]
sendAnonymousUsage = false
[log]
level = "DEBUG"
format = "common"
[providers]
[providers.docker]
endpoint = "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
watch = true
exposedByDefault = false
swarmMode = false
[api]
dashboard = true
debug = false
insecure = true
[entryPoints]
[entryPoints.insecure]
address = ":80"
[entryPoints.secure]
address = ":443"
[tls.stores]
[tls.stores.default]
[tls.stores.default.defaultCertificate]
certFile = "/ssl/wildcard.bv.stef.lan-crt.pem"
keyFile = "/ssl/wildcard.bv.stef.lan-key.pem"
¶ Repertoire ssl
Contient la clé et le certificat de *.bv.stef.lan qui sont utilisé par traefik pour la couche TLS
- wildcard.bv.stef.lan-crt.pem
- wildcard.bv.stef.lan-key.pem
¶ Lancement du stack
Lancer podman-compose.
L'utilisation de la commande est similaire à docker-compose.
stef@pod:~/pods/traefik$ podman-compose up -d
c51f58103bdec57bfa770cb7f084d4b5ac659ea14cd1c528565fa2b655183185
b6cf655a67b9bf9ffdf96d956d08e2ae37aa41c7ae40b8f268e3468bf1459ca3
traefik
d06b7635c26099c341690cf07b52def6507f843bc87a1d3750f7f91883929ef4
tinyauth
stef@pod:~/pods/traefik$ podman-compose ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
b6cf655a67b9 docker.io/library/traefik:latest --entrypoints.ins... 12 seconds ago Up 12 seconds 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:443->443/tcp traefik
d06b7635c260 ghcr.io/steveiliop56/tinyauth:v3 11 seconds ago Up 12 seconds 3000/tcp tinyauth
¶ Acces au dashboard Traefik
URL: https://traefikpod.bv.stef.lan/dashboard/
Tout les urls indiqués sont des alias DNS pointant vers l'addresse de la machine pod.bv.stef.lan
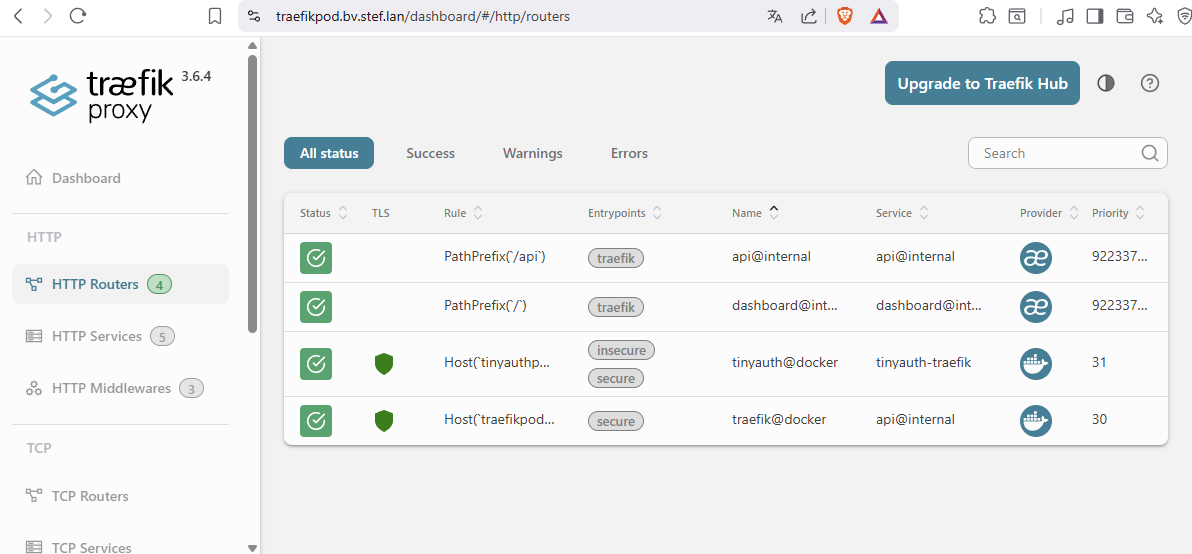
¶ Test de fonctionnement
Création d'un pod serveur web simple
podman run -d \
--name hello \
--network traefik \
--hostname hello.bv.stef.lan \
-l traefik.enable="true" \
-l traefik.http.routers.hello.rule=Host'(`hello.bv.stef.lan`)' \
-l traefik.http.middlewares.hello-https-redirect.redirectscheme.scheme="https" \
-l traefik.http.routers.hello.middlewares="hello-https-redirect" \
-l traefik.http.routers.hello-secure.entrypoints="secure" \
-l traefik.http.routers.hello-secure.rule=Host'(`hello.bv.stef.lan`)' \
-l traefik.http.routers.hello-secure.tls="true" \
-l traefik.http.services.hello.loadbalancer.server.port="8000" \
docker.io/crccheck/hello-world
stef@pod:~/pods/traefik$ podman ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
...
e37efca53ad4 docker.io/crccheck/hello-world:latest /bin/sh -c echo "... 2 seconds ago Up 3 seconds (healthy) hello
Treafik expose correctement le service
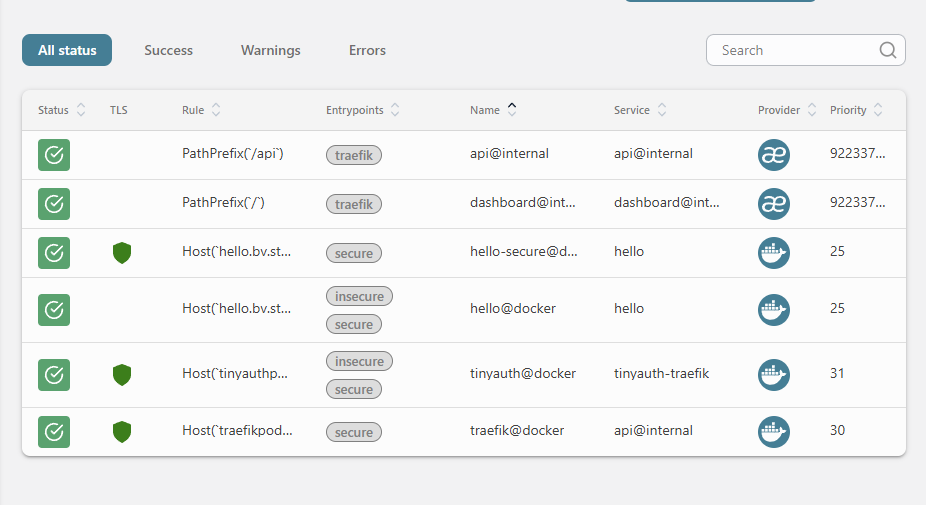
¶ Test accès applicatif
url: http://hello.bv.stef.lan/
La redirection http -> https est active
Le site est accessible:

¶ Vérification
Contrainement a Docker,les ports sont bien exposés avec l'utilisateur stef et non root.
stef@pod:~/pods/traefik$ lsof -i
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
rootlessp 12912 stef 10u IPv6 38057 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
rootlessp 12912 stef 11u IPv6 38058 0t0 TCP *:https (LISTEN)